Geographical RaaZ
201 POSTS
0 COMMENTS
Oceanography : Meaning , Nature and Scope
Meaning of Oceanography Oceanography is a scientific discipline that delves into the vast and complex world of our oceans. Covering over 70% of the Earth's...
Temperate Cyclones: Structural Characteristics
1. Introduction to Temperate Cyclones
Definition and Overview: Temperate cyclones, also known as extratropical or mid-latitude cyclones, are large-scale weather systems that primarily occur in...
Tropical Cyclone: Formation and Development
1. Introduction to Tropical CyclonesTropical cyclones are a type of intense storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, high winds, and heavy rain. They...
Cyclone and anticyclone
Cyclone and anticyclone
Cyclone and anticyclone: The Earth's atmosphere is a dynamic system, characterized by continuous movement and complex interactions between various elements. Two of...
Type of rainfall
Introduction to Rain: Type of rainfall
Type of rainfall: Rain is a natural and vital part of Earth's water cycle, a process essential for sustaining...
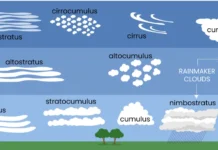
Types of clouds
Introduction to cloud: Types of cloudsTypes of clouds: Clouds are visible accumulations of tiny water droplets or ice crystals in the Earth's atmosphere. They...
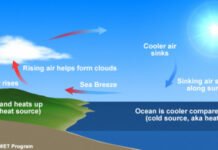
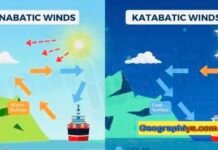
List of Local Winds
Introduction to Local Winds
Local winds are influenced by local conditions and geography. Local winds are more transient than global atmospheric circulation winds and can...
Types of winds
Introduction to Winds: Types of windsTypes of Winds: Wind moves air from high to low pressure. It is essential to Earth's weather systems and the...
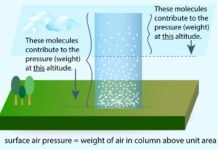
Belt of Atmospheric pressure
Introduction: Atmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressure, a fundamental aspect of Earth's meteorology, is the force exerted by the weight of the air above us. Measured in...
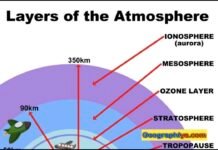
Structure of Atmosphere
Introduction: Structure of AtmosphereStructure of Atmosphere: The Earth's atmosphere is a thin layer of gases that surrounds the Earth, providing it with a unique...